Lawrence Lessig thinks it’ll all work out. I very much hope this is true.
For once a court fines or jails one recalcitrant officer, the rest will quickly fall into line.

Lawrence Lessig thinks it’ll all work out. I very much hope this is true.
For once a court fines or jails one recalcitrant officer, the rest will quickly fall into line.
I just sent the following to my representative in Congress via the web form on his page at the House website:
Based on media reports and what I can find on your website and twitter feed, it appears that you have not yet taken a stand against Trump’s illegal and unconstitutional executive order blocking entry by nationals from certain countries.
Can I count on you to do so in short order?
I didn’t mention in my note, but wanted to mention here, that Davis’s words for his constituents after the recent election invoked Lincoln’s phrase “With malice toward none, with charity for all,” so I’m a little concerned that he may be putting a dangerous strain on our nation’s limited supply of irony.
I also refrained from once again pointing out that the Republicans in Congress are straight-up cowards, afraid of widows and orphans.
What’s up with the very peculiar behavior of our new president and his bizarre insistence on telling lies that are easily detected as lies?
I’ve seen several suggestions about what might be going on. Two worth mentioning are Trump’s Constant Lying Is a Power Game and Hannah Arendt Explains How Propaganda Uses Lies to Erode All Truth. Both make the point that the purpose of the lie is not to fool anybody. Rather, it’s an expression of power.
Compelling people who know better to repeat your lies in their own words dramatically displays your complete control over them. Yes, there was a certain schadenfreude to seeing Christie and Rubio parroting Trump’s lies when they were angling for the VP slot or a cabinet post, but there are additional dangers in rendering even powerful people powerless—it means even more power is captured by the person at the top.
All of which is a bit tangential to my point, which is to recognize one good thing about this. Sad and disturbing as the situation is, these lies make it easy to find our allies: The news organizations that identify the lies and present them as such are on the side of right and truth.
Other strategies exist for identifying our allies, but most of them have turned out to be vulnerable to being co-opted by the bad guys.
This one is different.
Yes, an organization under the sway of the bad guys could attempt to do the same thing only backwards—call out the truth as a lie—but that’s pretty easy to spot. No one would be fooled for long.
They could, I suppose, call out actual lies as lies, and then (having built up some credibility) try to slip in an occasional falsehood as the truth, but that’s not going to be a successful strategy for the long term, unless maybe there’s a single issue that you really want to fool people about.
No, the strategy of calling out lies as lies will turn out to be uniquely available to the good guys, which means that we’ll be able to know which news organizations (and other organizations) are on the side of right and truth.
Sure, there’ll be a bit of extra work on our part—identifying the lies and documenting them, taking the time to pick a random few stories and digging into the data to see if the story is true (and the supposed lie an actual lie).
It’s important not to see that as pointless or hopeless work. It’s not like emptying the sea with a teaspoon, even if it may seem like that (because the supply of lies is vast and renewable). Think of it rather as collecting a bit of seawater for the purpose of making some artisan sea salt: The point is not to empty the sea, but to gather a bit of seasoning to use in the service of a larger project.
The larger project is what’s important, not emptying the sea. And there’s the bonus benefit that doing the work marks you as one of the good guys, and that’s something that’s good for all of us to know.
The “gig” economy: all the sorts of work arrangements where you’re not a permanent employee and can’t expect that work one day implies that you’ll have work the next day—freelancing, contracting, temp work, casual labor, and most recently, software-mediated contract work like Uber driver.
These sorts of work have been growing as a fraction of all work. In fact, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, in the last ten years contingent workers have gone from being 10% of the workforce to being 16%. In fact,
all of the net growth in aggregate employment in the decade leading up to 2015 can be accounted for by contingent work arrangements, which means there has been no net employment growth in traditional work arrangements.
Source: FRB: Brainard, The “Gig” Economy: Implications of the Growth of Contingent Work
This matters to everyone with an interest in the U.S. economy, but it matters particularly to the Federal Reserve, which is charged by Congress to:
promote effectively the goals of maximum employment, stable prices and moderate long-term interest rates.
Source: The Federal Reserve’s Dual Mandate
So this raises the question: Does strong growth in the number of freelancers, on-call temps, and Uber drivers mean that we’re getting closer to maximum employment? Or, that we’re getting further away?
This sort of thing was a fantasy of mine, back in the 1980s. I could see things getting worse in the US, and the idea that a foreign passport and foreign residency could provide an escape if things got too bad was pretty appealing.
Nowadays not so much. It’s not that things have gotten better in the US; it’s that things have gotten worse other places at least as quickly. More to the point, things getting worse in the US seems to make things worse other places, so the conditions that make the idea appealing are the same conditions that make it pointless.
One book that substantially influenced my thinking in this area is Emergency: This book will save your life by Neil Strauss. I recommend it highly. In entertaining and informative prose, he documents his transformation from just the sort of kook I was in the 1980s into somebody with a much more practical perspective.
Still, an EU passport might have its upsides. Anybody got a spare quarter million euros and an interest in learning Greek? (If money is no object, a half million euros will let you buy in to Ireland, and I expect learning Gaelic is optional.)
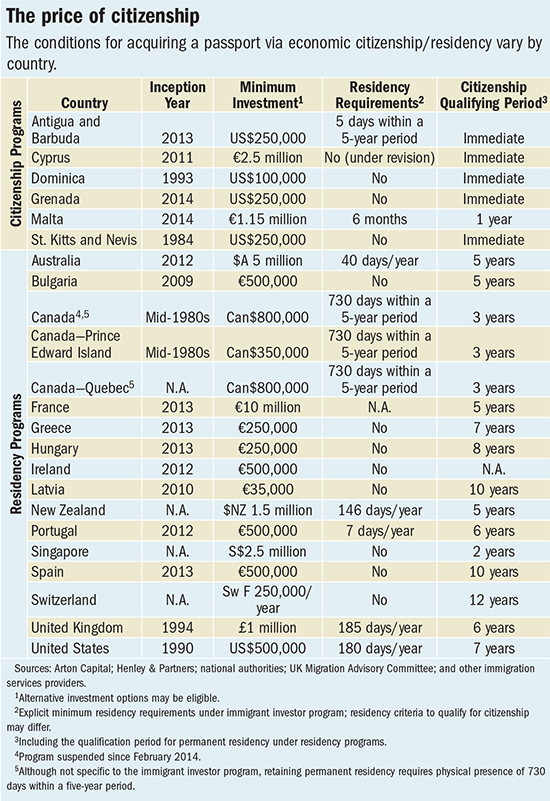
Graphic from Citizenship for Sale on the International Monetary Fund’s IMFDirect blog.
I have long opposed most sorts of gun control. The main reason is the same reason I oppose drug prohibition: There is no way to enforce a ban on a thing, except through police-state tactics (and I don’t like living in a police state).
How do you ban a thing? You can pass a law against possession, but that law is unenforceable except by house-to-house searches. You can’t even enforce a ban on carrying concealed weapons except by stopping and frisking everyone out on the street. (Please don’t suggest only stopping and frisking “suspicious” people, unless you have first-hand experience with looking like one.) Since there’s no victim to report the crime (“I was illegally possessed at!”), you only find the criminals by chance, unless you’re willing to go full war-on-drugs with undercover agents, coerced informants, wiretaps, search warrants executed by SWAT teams and so on.
You could impose a high penalty on possession of a gun, and then only enforce the law when a gun came to the attention of the police. That would probably get the guns off the street—a gun hidden under the floorboards isn’t much of a threat—except of course for the “only criminals will have guns” issue: High penalties don’t much deter people who are already committing crimes with high penalties. Plus, it leads to all the classic slippery-slope arguments. Selective enforcement (searches used to harass disfavored people) and unfair results (unlucky people spending 20 years in prison for a gun they didn’t know was in the boxes of grandfather’s personal effects) being just two of the downsides.
Besides, guns are useful tools. If we have a ban that applies as well to the police and the military, then we’ve denied them tools that they may need to do their jobs. But if the ban doesn’t apply to them, then we have to draw the line in a specific place—or a series of specific places. If police qualify, how about campus police? Transit police? Park rangers? Do bodyguards qualify? How about armored-truck guards? Stalking victims? The result is once again selective enforcement and unfair results, this time with a side order of political shenanigans. Some people who need the tool will be denied it. Other people who thought they were allowed the tool will have their lives destroyed when a court rules that they were not.
Much more sound than laws against things is laws against behavior. It’s illegal everywhere to shoot someone or to threaten someone with a gun or even to discharge a gun in a populated area. These are the sorts of laws that gun-control opponents always point to as the right way to control guns. But they self-evidently don’t work. Even if you discount suicides and accidents, there are 12,000 homicides a year in the United States—with about 90% committed with a firearm.
So, what other behaviors could we regulate? There is often talk of regulating the sale of firearms. Being in the business of selling firearms is already extensively regulated, but currently it’s legal to sell (or give away) a firearm without being in the business—sales between friends and gifts between relatives are legal, and don’t require that you be a licensed firearms dealer. That could be changed. You could make selling firearms be like selling prescription drugs, which only a licensed pharmacist can do. Many currently legal, perfectly ordinary behaviors would be illegal, or else the laws would have to be very carefully drafted. Could a father buy his son his first .22 rifle? Could an Olympic-champion riflewoman let her aspiring-sharpshooter daughter take mom’s match-grade pistol to the shooting range to practice with? If a down-on-his luck man pawned a family heirloom firearm, would he be committing a crime if the pawn shop owner’s firearms license were not in order? What if the pawn shop clerk were a felon?
Registering guns is often proposed, although I don’t see how doing so would reduce violence. Further, I think gun-owner fears of gun registries being useful primarily as a tool for eventual confiscation is well-founded: What other use would a registry have? The parallel is less with registering cars (which are big and operate in public where people can see them) and more with registering typewriters (which are small and are generally used in private).
Illinois has long had a registry of “allowed gun buyers,” which is somewhat less pernicious than a list of guns: It would still provide a list of places to search, if things trended even further toward a police state, but it would do so without providing what amounts to a master of list of guns to be seized. In fact, I would fully support such a scheme, if it were automatic: Every adult who has not been convicted of a felony or violent misdemeanor, nor adjudicated as dangerous or incompetent in some other fashion, should be on the list of those allowed to buy guns. The government could automatically strike people from the list upon conviction or commitment to a mental institution (with an appropriate appeals process to correct errors). Or people could file a simple form to ask to be taken off the list, if they had some personal objection. It’s basically the instant background check from the opposite direction.
I will say this, though—gun control advocates are finally on the right track, in attempting to mobilize public opinion. For the past thirty years, members of a small, mostly liberal elite have been trying to use their influence over government officials to pass gun control. But with public opinion so divided, legislative sausage-making has produced laws that are pointless and ineffective, full of easily ridiculed loopholes, but still with traps for the unwary gun-owner to commit a technical violation that leads to harsh sentences, without reducing the number of guns or making them less dangerous. (I am thinking in particular of the so-called assault rifle ban that ended up merely banning a handful of cosmetic details.)
And yet, I am nearly brought around. I am ready to support gun control legislation, if something can be found that would actually reduce violence (or at least its severity), doesn’t require police-state tactics to enforce, and doesn’t send people to prison simply because their papers are not in order.
That last is non-negotiable for me, an attitude puts closer than I’d like to be to unsavory company on other issues, such as immigration, where I agree with many Republicans that I think we should control our borders better. It’s because the other tactics of keeping our population density low are ineffective, unless we empower the police to check people’s papers. If we want the higher standard of living that comes from living well below carrying capacity—and I do—we can’t let just everybody live here. But having a category of “illegal” people forces immigrants to live outside the rules that promote the health, safety and prosperity of everybody, for fear of deportation. That risks the health, safety, and prosperity of all of us.
I’m no happier with letting police demand my firearm paperwork, and send me to prison if it’s not in order, than I am with letting police demand my citizenship papers against similar consequences.
I also think playing with guns is fun, and would be sad if they were banned. But I would give up playing with guns, if I thought it would prevent a large fraction of 11,000 murders a year. I don’t see a clear path from here to there, but I have joined the mass of people trying to find one.
People are making a big deal right now about how it’s obviously stupid that “suspected” terrorists can buy guns, but can’t get on planes. But nobody seems to be pointing out how it’s terribly unamerican that there’s even a category of “suspected” terrorists.
Until 15 years ago, you were presumed innocent until you were convicted of a crime. Yes, there was a category of “indicted” that was kind of in-between—but there was a clear legal process for how you got there, and a clear path to resolving the in-between state.
I really object to the idea that someone who has been convicted of no crime can be put into a category that denies them any of their constitutional rights. The gun nuts are putting a special premium on the right to be armed, but what about the right to travel?
The government, in the few court cases that have had at least some proceedings so far, has put a lot of weight on the idea that you don’t have to be able to fly to exercise your right to travel. You can still walk, after all. If you’re overseas you can buy a yacht and sail to the U.S, and the lawyers for the government seem to think that resolves the right-to-travel issue.
The fact that the process for getting into this state of “not convicted of a crime but still lack the rights of a normal person” is opaque and uncontestable is bad, but really doesn’t bother me as much as the state existing at all.
I am slowly coming around on the gun-control issue, but I wouldn’t mind preserving the status quo just for a bit, as a way to focus the mind on the broader issue: We used to have constitutional rights, and nowadays the most basic of them—being deprived of liberty without due process—has been constantly violated for fourteen years.
I’d seen it right along, and plenty of other people have commented on it before me, but I don’t think it really sunk in until just this past week, with all the hand-wringing over Syrian refugees:
Republicans are a bunch of cowards.
I’ve never seen so much fear as has been on display the past week from the Republicans (and, I must admit, way too many Democrats as well). And over what? A bunch of people—largely educated and middle class—who have been forced to flee their homes.
Seriously, the Republicans are straight up afraid of widows and orphans. What’s up with that?
I mean, I totally understand why the Syrians are afraid. They have soldiers and militias fighting house-to-house in their neighborhoods, blasting them with artillery, even using chemical weapons. Not to mention, they have U.S., French, and Russian air forces dropping bombs on those same militias, in the same neighborhoods.
But the Republicans? What are they afraid of? They’re afraid that some “terrorist” will “slip in” amongst the masses of refugees and commit “acts of terror” in the United States.
Well, these hypothetical refugee-terrorists (of which we’ve seen exactly zero so far) will have to get at the back of a pretty long line, behind the non-hypothetical white-supremacist, right-wing, and anti-government militias (not to mention depressed loner high-school boys) who have been committing mass murders in the U.S. in numbers well in excess of those committed by foreign terrorists.
Perhaps worst of all, most of the Republican rhetoric isn’t even aimed at affecting government policy; it’s aimed at preemptively setting up other people to take the blame. “We said you had to give ‘100% assurance’ that they wouldn’t be terrorists before you could let them in, so if even one of them commits a terrorist act it’s all on you!” (They know perfectly well that ‘100% assurance’ is impossible, which is why they demand it. It makes me want to point out that in the U.S. we convict people of capital crimes and execute them, and all we require is assurance “beyond a reasonable doubt.” I expect pointing that out makes me a rose-colored glasses wearing liberal who’s endangering our country.)
Fortunately, some people are man enough not to quake in their boots at the idea of some ordinary families fleeing terror and ending up here, and man enough not to be terrorized at the idea that they might have to take the blame if an evildoer does slip in. I’m thinking of President Obama here, rather too few Democrats in Congress, most of my liberal friends, and (oddly, because I don’t think of myself as especially brave) me.
I got email today from one of my senators, with the text of a truly appalling letter to president Obama from the senator and eleven of his colleagues.
The letter (here’s his press release on it) calls on the president to ensure that “no refugee related to the Syrian crisis is admitted to the United States unless the U.S. government can guarantee, with 100 percent assurance, that they are not members, supporters, or sympathizers of the so-called Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS).”
It’s obviously intended to be an unattainable threshold, but that’s really beside the point—the whole thing is completely wrong-headed.
I was moved to respond, and sent him this message via the contact form on his website:
I wanted to say that I was appalled by the letter to president Obama that you shared with me.
Since 9/11, the number of refugees who have committed terrorist attacks in the US is exactly zero—which suggests to me that keeping refugees out of the US is a complete waste of time and effort.
Targeting refugees—the most helpless and vulnerable among us—is not only pointless, it is also heartless and cruel. It is a failure to live up to our obligations under international law. It is also, in my opinion, terribly unamerican.
There are far better, far more effective ways to protect US citizens than by heaping yet more misery on those who have already faced the violent extremism of ISIS—those Syrians who have been forced by it to flee their own country.
I urge you to write to the president and let him know that you repudiate your entire letter, and to suggest that existing US policies on refugees, established in accordance with international law, should remain in place.
Another eleven senators signed the letter. If yours was one of them, you might want to contact your senator and say something. Feel free to borrow from my text, if it speaks to you.
What’s the big deal with Flickr making commercial use of creative commons licensed photos that were licensed for commercial use? What did people think they were doing when they licensed their photos?
I have a bunch of photos licensed with the attribution license, and a few have been used many times. Here’s my most popular:
That image has been used thousands of time, mostly on financial websites, but also lots of other places, including printed publications. This is just what I had in mind when I licensed it. (Click through and read the comments—a few of the people who used it posted to thank me.)
When I first started writing posts at Wise Bread, I tried to take most of my own pictures. I did that for a couple of reasons. One was so I could get the picture I wanted; at least as important was so that my photos would be unique. (So many financial sites used the same few stock photo sources, so readers pretty quickly started seeing the same images over and over.)
When I didn’t think I could create an image of my own, my go-to source for alternatives was creative commons licensed photos on Flickr.
Before I started using creative commons licensed photos myself, I’d put a creative commons license on some of my images, but was inclined to use a more restrictive license, including non-commercial. After all, I figured, if someone was making money off it, didn’t I deserve a cut?
But for use on Wise Bread, since I was making money, I figured that I shouldn’t use images marked non-commercial. And I was surprised and pleased at just how many people shared their images without that restriction.
I was so grateful, I started licensing most of my photos with an “attribution” license, meaning that I was allowing commercial use—just like the use I was making of other people’s images. (Some photos I didn’t license—mostly those with pictures of people. Properly speaking, a creative commons license is silent on the issue of a model release, but most people don’t think about it when they use an image, and I didn’t want to be in the position of enabling that behavior.)
My point here is simply that I knew what I was doing—and I would certainly hope that everyone else who used a creative commons license did as well. If you license a photo for use with an attribution license, you are explicitly permitting commercial use. It seems bizarre to complain about it when it happens. What did you expect?
Because I think it’s a somewhat nicer photo, I thought I’d also share my second most-used creative commons licensed photo on Flickr:
Believe me, I didn’t choose the license without thinking about it. Anyone may use my creative commons licensed photos, in accordance with the terms of the license.
That includes Flickr, and Yahoo. Duh.