I don’t usually worry much about investment bubbles. There have been a lot of them over the past few hundred years, and most of them (railroads, telegraph, dotcom…) were expensive disasters largely only for the people who invested in them. Some though, such as the Great Financial Crisis of 2007–2009, were expensive disasters for lots of other people as well. So it’s worth thinking a bit about whether the current AI bubble is of the former sort or the latter—and how to protect your finances in either case.
Bad just for investors
One big difference between bubbles that are going to be wretched for everybody when they pop and those that’ll end up mostly okay except for the foolish investor’s portfolio, is whether the excess investment got spent on something of enduring value.
For example, railroad lines got enormously overbuilt in the 1840s in the UK and in the 1880s in the US, leading in both cases to a stock market bubble, followed by a stock market crash and a banking panic. But (and this is my point), the enormously overbuilt railroads were of some value. As the firms went bankrupt, the people who had over-invested lost a lot of money, but the railroad tracks, rights-of-way, and rolling stock all still existed. The new firms that got those assets, free of the excess debt, were often viable firms that went on to be successes—hiring workers, providing transportation, and eventually providing a return to the new investors. The people who got screwed were the old investors. (And not even all of them, as the original investors often saw the overbuilding happening early and sold out just as the clueless people who knew nothing about running a railroad, but just saw stocks soaring and wanted to get in on it, started piling in.)
Much the same was true of part of the dotcom bubble. A lot of money got spent on a lot of things. To the extent that it was spent on buying right-of-way and burying fiber, there was something of enduring value that ended up owned by somebody, making it one of the less-bad bubbles.
The key to avoiding catastrophe in bubbles of this sort is largely just a matter of not investing in the bubble yourself.
Bad for the economy
But some bubbles have produced horrible, wretched, prolonged difficulties for the whole economy. The other part of the dotcom bubble, besides the dark fiber build-out, was the bubble in companies with no profits and no prospect of ever having profits, whose stock prices went up 10x based on nothing but a story that sounded compelling until you thought about it for 10 seconds. As usual, that ended up being very bad for the people who invested in those companies, but it also was bad for the whole economy, because when those firms went bankrupt, they left behind nothing of enduring value.
The result was that the imagined wealth of those companies just vanished. The stock market went down, which was bad for (almost) everybody, and it produced a general economic malaise, because post-dotcom crash it became hard even for legit companies with real assets, a real profit, and a real business plan for growth, to raise money, which made actually producing that growth much harder.
Really bad for the economy
There is, however a step beyond just pouring a bunch of money into a bubble that doesn’t actually produce anything of enduring value, like a fiber optic network or a railroad. That’s when the money is raised with leverage (i.e. debt).
The 1929 stock market crash was a rather drastic example. People invested in stocks not because there was an underlying business that was worth what the investors were paying for it, but purely because the stocks were going up. That might have been okay in other times, but stock brokers had recently started allowing ordinary people (as opposed to just rich people) to buy on margin—where you just put up a fraction of the price of the stock you want to buy, and the broker lends you the rest.
In the 1920s you could buy on 90% margin, where you only put down 10% of the price of the shares. That meant that, if the stock price went down by just 10% your whole investment was wiped out, and the broker would sell you out to raise money to pay off (most of) the loan. And of course, all those sales into a falling market produced more losses, leading to the crash.
Since the 1930s you could only buy stocks on 50% margin, making it much less likely that your broker will sell you out into the teeth of a general stock market crash—although it can still happen.
Bubbles with leverage
A great example of a bubble with leverage is the Great Financial Crises of 2007. (Most people date it from 2008, because that’s when Lehman Brothers collapsed. I date it from 2007 because that’s when my former employer closed the site where I worked and I ended up retiring rather earlier than I’d planned.)
That was a particularly bad bubble. A whole lot of money was raised, with leverage, to buy housing. But very little of the money ended up being spent to build more housing (which would have been something of enduring value that would have lasted through the subsequent collapse). Instead, the money was spent bidding up the prices of existing housing, which then fell in value after the bubble popped.
So we had two of the classic producers of bad bubbles: Nothing of enduring value created, and leverage. The whole things was made even worse by the structure of the leverage in question.
This is getting rather far from my main point, so I won’t go into much details, but to raise the large amount of money that was going into houses, the rules on housing market leverage were being eased over a period of time. It used to be that you had to put 20% down on a house. Then you still had to put 20% down, but only half of it had to be cash, with the other half being funded with a second mortgage on the property (at a higher interest rate). Then they started letting people put just 3% down. Then they started letting people with good credit put nothing down. Then they started letting people with no credit put nothing down. At the same time, “structured finance” obscured just how risky all those mortgages were, meaning that when the bubble went pop lots of “mortgage-backed securities” ended up being worth zero.
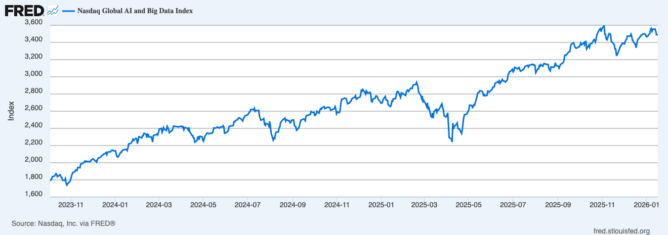
Which kind is the AI bubble?
This brings us to the current AI bubble. A whole lot of money is pouring into building two things:
- Data centers (buildings filled with computer chips of the sort used to train and run AI models)
- Large language models (non-physical things that are basically just a bunch of numeric weights of a bunch of tokens which can be used to produce streams of plausible-sounding text)
Each of those may have some enduring value.
Data centers will have some. They will probably have a lot less than a network of fiber optic cables, which can be buried and will have value for decades with minimal cost or maintenance. Since newer, faster chips are coming out all the time, a data center is well behind the cutting edge as soon as it’s finished. Plus, training or running an AI model runs those chips hard, meaning that they probably only last a couple of years (due to thermal damage on top of regular aging).
Large language models probably have even less enduring value, because so many people are training new ones all the time. People are always trying to make them bigger (trained on more data) while also making them smaller (so they can run without a giant data center). All that means that your two-year-old LLM probably isn’t worth what you paid to build it, and a four-year-old LLM probably isn’t worth anything.
That’s how things looked a year or so ago—a perfect example of a bubble that would burn the people who sank money into it, but leave the broader economy untouched.
Sadly, that’s been changing.
First, the structure of the leverage has been changing. It used to be rich people and rich companies were building data centers and hiring software engineers to build LLMs. But lately that’s been getting screwy. Those large companies are raising off balance-sheet money with Special Purpose Vehicles (small companies that big companies create and provide some capital to, that then borrow a bunch of money to make something, with the loans collateralized by the things they’re making—but importantly, not an obligation of the big company that created them). Any particular SPV can blow up, if it turns out that the things it built don’t earn enough to pay the interest on the money the borrowed to build them. And large numbers of SPVs can blow up if financial conditions change to make it harder for all the SPVs to roll over their debts as they constantly have to keep their data centers running.
Second, they’re also engaging in weird circular investing and spending arrangements, where company A buys stock in company B which then turns around and pays all that money back to company A to buy chips, letting company A treat it as both income and an investment, while company B can pretend it got its chips for free.
Finally, there’s all the non-financial obstacles that may well throw a wrench into the whole thing. The fact that LLMs are all built on copyright violations. The fact that running data centers requires huge amounts of power and water (that has to be produced and paid for). The fact that producing that water and power brings with it horrible environmental impacts.
What to do
So, if AI is a bubble, and its one of the bad sort that will produce a panic and a recession when it pops, what should you do?
There are a lot of little things you can do that will help. I wrote an article with suggestions at Wise Bread called Are your finances fragile? It talks about what financial moves you can take to put yourself in a better position if there’s a general financial crisis. (If you’re interested in my writing about this stuff more broadly, I wrote a overview of my perspectives on personal finance and frugality called What I’ve been trying to say, that includes a bunch of links to other of my posts at Wise Bread.)
Besides that general advice, there are also a few things to strictly avoid. In particular, strictly avoid thinking that you can find some very clever investment strategy that lets you make money off the popping of the bubble. Yes, after the fact there will be some investments that make a lot of money, but no amount of keen insight will let you find and make those investments, as opposed to the thousands of very reasonable-seeming investments that will blow up just like all the rest.
Along about the end of the Great Financial Crisis I wrote an article called Investing for Collapse, which explains why any such effort is pointless. It holds up pretty well, I think.
Short version? Avoid debt. Keep your fixed expenses as low as possible. Build a diversified investment portfolio that limits your exposure to the most obviously stupid investments, but doesn’t do anything too weird or wacky in an effort to get them to zero—it’s pointless, and will probably do more harm than good.
Good luck when the AI bubble pops!